Home / news
News
Flexible IT Infrastructure: From Burden to Advantage
Old Paradigm VS New Paradigm

For years, many companies in Indonesia and global companies still believe that investing in IT infrastructure is synonymous with high initial costs (Capital Expenditure/CAPEX). They have to purchase physical servers, storage, network devices, software licenses, and even rent special rooms with cooling and backup power to keep the system running. Not to mention, companies also have to factor in the cost of an operational team or human resources (HR) to keep this infrastructure running smoothly. Although the infrastructure is expected to be used for 3-5 years, this approach is no longer in line with dynamic business needs. The challenge is that high investment costs reduce financial flexibility, as inaccurate infrastructure capacity often results in under-provisioning or over-provisioning.
This change is becoming increasingly apparent in Indonesia. According to a PwC survey (2022), cloud adoption in the small and medium-sized business (SMB) segment has reached 89%, while among large companies, 80% are already using cloud technology, with the rest planning to adopt it within the next three years. This data shows that many organizations in Indonesia are beginning to switch to cloud infrastructure, leaving behind the traditional on-premise model. Furthermore, the economic impact of cloud adoption is also significant. The PwC survey estimates that cloud adoption could add around USD 10.7 billion to Indonesia's economy in the 2021–2025 period. The fact that the cloud can drive productivity and digital transformation further reinforces organizations' choice of flexibility and operational efficiency.
Complementing this data, Indonesia's cloud market projections are increasingly optimistic. Its value is estimated to reach USD 2.09 billion in 2024 and increase to USD 4.80 billion in 2032, with an average annual growth of around 14.5%. This phenomenon shows that many organizations in Indonesia are beginning to abandon traditional infrastructure approaches (purely on-premise) and are shifting to more flexible models, both public and hybrid cloud. In line with this trend, AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers a new paradigm through its Pay As You Go (PAYG) based Operational Expenditure (OPEX) model. With this model, companies do not need to purchase physical devices, but only pay for resources according to usage. As a result, IT investments become much more efficient, adaptive, and profitable, in line with the digital transformation that is currently taking place in Indonesia and around the world.
The Pay As You Go (PAYG) Concept in AWS
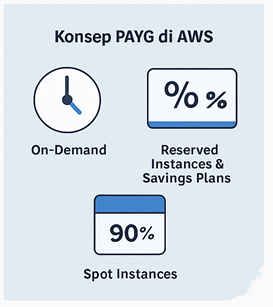
The PAYG principle is very simple: only pay for what you use, nothing more. For example, if a server runs for 10 hours, the company only pays for 10 hours, not the full 24 hours or a full month. When the server is turned off, the charges also stop running (except for storage components such as Elastic Block Storage/EBS, which continue to be used). In AWS, PAYG comes in several options:
- • On-Demand Instances – pay per hour or per second for computing.
- • Reserved Instances & Savings Plans – save up to 70% on costs for long-term commitments (1 year or 3 years).
- • Spot Instances – take advantage of unused EC2 capacity on AWS at discounts of up to 90% compared to On-Demand Instances, suitable for flexible workloads (such as stateless, fault-tolerant, or flexible workloads like big data, containerized workloads, CI/CD, web servers, high-performance computing (HPC), and test & development).
This model makes IT costs highly dynamic. Gone is the concept of “buying excess servers just in case.”
AWS Infrastructure Flexibility
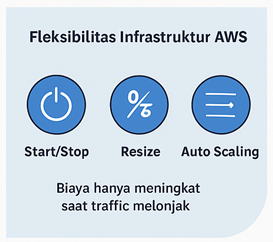
In addition to being cost-effective, PAYG also makes infrastructure much more flexible. This flexibility comes in three main forms
1. Start/Stop Instances
- Virtual servers (Amazon EC2) can be turned on only when needed. For example, for a development environment that is only used during working hours, the server can automatically shut down after 6 p.m. and turn back on at 8 a.m.—without manual intervention.
2. Resize Instance
- Server capacity can be easily adjusted. When the workload increases, the company can simply scale up to a larger instance with just a few clicks or a single API command. Once the workload decreases, the server can be scaled down again.
3. Auto Scaling Group (ASG)
- ASG automatically adds new servers when traffic spikes, then scales back down when traffic subsides. As a result, costs always align with actual needs—no more waste.
Imagine a new e-commerce startup in Jakarta. When the application was first launched, visitor traffic was still low, easily handled by a simple server costing only hundreds of thousands of rupiah per month. However, when they held a major discount campaign such as Harbolnas, the number of visitors skyrocketed thousands of times. If they still relied on on-premise servers, they would be overwhelmed. The server could crash, shut down, or even go down due to overload. Meanwhile, adding new servers takes weeks—too late to keep up with the traffic surge. Servers are automatically added. Once traffic returns to normal, the servers automatically decrease. Costs only increase when they are actually needed. Another case study example is a manufacturing company that has been around for decades and initially used its own data center. They purchased large servers every 5 years. Problems arose during the COVID-19 pandemic: the need for remote access skyrocketed, but server capacity was insufficient. They eventually moved to AWS with a PAYG model. Now, they no longer need to purchase servers every five years. Infrastructure can be scaled up or down according to business needs. In addition, data security has also improved with AWS Security services.
Business & Technical Benefits
Using PAYG on AWS provides many benefits:
- • Cost efficiency – no large upfront investment.
- • Agility & innovation – infrastructure can change in minutes.
- • Reliability – AWS services are distributed across multiple Availability Zones.
- • Sustainability – more environmentally friendly because it uses energy-efficient shared infrastructure.
6 Pillars of AWS Well-Architected
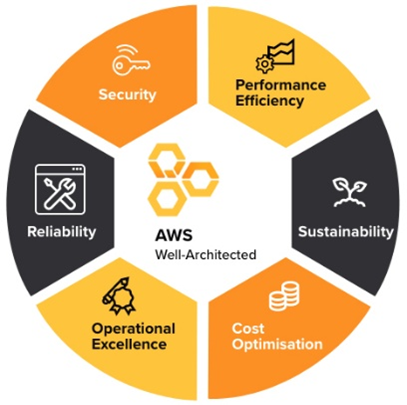
The PAYG model supports the six pillars of the AWS Well-Architected Framework:
1. Operational Excellence
- With a pay-as-you-go model, companies can more easily manage servers. Turning them on, turning them off, or adding capacity can be done automatically—like turning on a light with a switch. As a result, IT teams are no longer bogged down with minor tasks and can focus on improving services.
2. Security (Data Security)
- Even with flexible costs, security is not compromised. Data remains protected with encryption systems, strict access controls, and international security standards. So, even if you don't buy your own server, your company's data is still as secure as if it were stored in a “digital safe”.
3. Reliability (System Reliability)
- Traditional servers often experience problems when there is a sudden surge in load. With PAYG, the system can automatically increase capacity when needed. Even if there is a disruption in one location, the service can be transferred to another location to keep running. It's like having an automatic generator when the power goes out—services stay up and running without interruption.
4. Performance Efficiency
- PAYG allows companies to place applications in the location (region) closest to users. This means faster access, better application response, and an improved user experience. It's like choosing the closest highway to reach your destination faster.
5. Cost Optimization
- This is the essence of PAYG: only pay for what you actually use. No more idle server costs. It's like paying for electricity or water—you only get billed for what you use, not a fixed monthly fee.
6. Sustainability (Sustainability & Environmentally Friendly)
- By using more efficient shared infrastructure, energy consumption is reduced compared to if each company built its own data center. This helps reduce carbon footprints and makes companies more environmentally friendly.
Challenges & How to Overcome Them
Of course, there are challenges because costs can suddenly skyrocket if not managed properly. Many companies are surprised because they forget to turn off servers or don't set cost alarms. Fortunately, AWS provides solutions such as Cost Explorer, Budgets, and tagging to keep expenses under control. With proper management, the PAYG concept in AWS makes infrastructure cheaper, more flexible, and more profitable. Companies no longer have to be tied to large upfront investments, but can simply adjust costs according to actual needs.
This is where PT Mastersystem Infotama Tbk (MSTI) comes in to help customers manage AWS, providing 24/7 real-time monitoring and consultation to ensure optimal AWS usage.
Newsletter - Stay tune and get the latest update
Far far away, behind the word mountainsCopyright ©2024 All rights reserved | PT Mastersystem Infotama
